- Details
MDNR Report

Allegan is now the 17th Michigan county where chronic wasting disease has been identified in the wild deer population, according to the Michigan Department of Natural Resources. An emaciated doe reported by residents of Leighton Township recently tested positive for the disease.
CWD was confirmed by the Wisconsin Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory. The sample was also sent for a secondary confirmation to the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Veterinary Services Laboratory in Ames, Iowa, but results may be delayed due to the federal government shutdown.
CWD is a fatal neurological disease that affects white-tailed deer, elk and moose. To date, the disease has also been detected in the following Michigan counties: Clinton, Dickinson, Eaton, Genesee, Gratiot, Hillsdale, Ingham, Ionia, Isabella, Jackson, Kent, Mecosta, Midland, Montcalm, Ogemaw and Washtenaw.
The declining health of this 1.5-year-old doe was first noted by private landowners in late summer. In late September, the DNR was contacted and authorized humane euthanasia and collection of the deer. On exam at the DNR’s Wildlife Disease Lab, the deer was noted to be in poor physical condition with no body fat.
“The care that’s demonstrated when people take the time to share their observations is a critical contribution to our disease-testing efforts,” said Brent Rudolph, DNR deer, elk and moose management specialist. “Public reporting of deer that appear unhealthy is very important for identifying CWD that may exist at low levels in previously undetected areas.”
CWD is a chronic, slow-developing disease that spreads slowly across the landscape. It has been detected in Kent County, adjacent to Leighton Township, which is in the northeast corner of Allegan County. Allegan County was under focused CWD surveillance in 2021, when approximately 500 deer were tested, with none testing positive. The DNR has continued to test deer that appear sick in Allegan County when possible. Hunters can get their deer tested with a free CWD self-sample submission kit from the DNR.
Deer that appear emaciated, lethargic, disoriented, lame or unresponsive are good candidates for CWD testing, though these symptoms are characteristic of deer affected by other maladies or injuries as well. The public is encouraged to report sick deer at Michigan.gov/EyesInTheField.
Safety recommendations
To date, there have been no reported cases of CWD infection in people. However, as a precaution, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that infected animals not be consumed as food by either humans or domestic animals.
Hunters should take precautions when field-dressing or processing deer: wear rubber gloves, minimize contact with the deer’s brain and spinal tissue, and wash hands with soap and warm water after handling any parts of the carcass.
Proper disposal of deer carcasses is critical to prevent the spread of chronic wasting disease. Deer carcasses and parts should go directly to a landfill or be disposed of through regular bagged trash pickup. Studies show that CWD can survive on the landscape for years, contributing to the spread of disease. Deer harvested from known CWD areas should never be disposed of on the landscape.
Testing options for hunters
There are several testing options available to hunters, depending on their hunting location. In 2025, focused testing will continue in Baraga, Chippewa, Dickinson, Houghton, Iosco, Keweenaw, Luce, Mackinac, Ogemaw, Ontonagon and Schoolcraft counties in the Lower and Upper peninsulas. More information on CWD testing in these counties and a link to find DNR drop boxes and staffed sample submission sites are available on the CWD testing webpage.
Free self-sample submission kits have been available in limited areas for the last three years. Beginning in 2025, these kits are now available in all counties outside of the DNR bovine tuberculosis (bTB) or CWD surveillance areas. Kits allow hunters to remove lymph nodes and ship them directly to the MSU Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory at no cost. Hunters can pick up a kit at a local distribution site. If hunters choose not to pick up a kit, testing is available for a fee through direct submission to a cooperating USDA-approved diagnostic laboratory.
All deer from counties with previous confirmed cases of CWD or bTB that are donated to the Hunters Feeding Michigan program are also submitted directly to the MSU lab for testing.
The DNR’s work with researchers and hunters to detect and slow the spread of CWD is possible because of limited general fund dollars allocated by the Michigan state legislature.
Michigan’s CWD testing strategy
Since chronic wasting disease was first detected in Michigan's wild deer in 2015, more than 110,000 deer in Michigan have been tested for CWD through a variety of efforts, including responding to public reports of sick deer and focused testing of hunter-harvested deer. In total, more than 144,000 wild deer have been tested through DNR surveillance efforts that started in 2002, with 265 CWD-positive deer identified. In addition, since direct hunter submissions of deer to the MSU lab began in 2020, more than 3,400 submitted samples have yielded 61 additional confirmed positives.
After initial intensive testing near areas of the first CWD detections in the state, the DNR began a rotational approach to testing harvested deer in 2021. A group of counties is selected each year, with the eventual aim of testing enough deer in every Michigan county. The goal of this approach is early disease detection, as management has the potential to be most effective when the disease is caught early. This method also provides confidence that if the disease does exist in these areas but goes undetected, that it is most likely there at a very low level.
For more information on chronic wasting disease, visit Michigan.gov/CWD.
- Details
MDNR Report
The Michigan DNR is alerting anglers that the ports of Grand Haven, Muskegon and Whitehall/Montague are covered by new regulations restricting allowable fishing gear at these locations from Nov. 1 to Nov. 30.
The goal of these regulation changes (approved by the Michigan Natural Resources Commission in Fisheries Order 202.25) is to protect spawning lake whitefish by reducing snagging, as well as overall harvest of adult lake whitefish in these areas.
Lake whitefish populations in Lake Michigan are in decline, due to pressures from invasive zebra and quagga mussels, which have altered the food web of the Great Lakes.
Based on angler creel survey data, much of the harvest of lake whitefish in these areas is from snagged fish. The new gear restrictions address snagging, which should reduce the overall harvest of lake whitefish.
“Lake whitefish numbers have been in decline in Lake Michigan since the late 1990s,” said Jay Wesley, the DNR’s Lake Michigan Basin coordinator. “Lowering harvest in November will help protect spawning adult lake whitefish while continuing to allow this unique angler opportunity."
If the new gear restrictions are not effective at reducing harvest, fisheries managers may consider recommending a lower daily possession limit of lake whitefish.
The locations under these regulations include the port of Muskegon from the westernmost pier head extending into Lake Michigan (excluding break walls) to the easternmost pier head extending into Muskegon Lake; the port of Whitehall/Montague from the westernmost pier head extending into Lake Michigan to the easternmost pier head extending into White Lake; and the port of Grand Haven from the westernmost pier head extending into Lake Michigan to the U.S. 31 bridge (northbound Beacon Boulevard).

At these ports, it is unlawful to use other than one single-pointed unweighted hook measuring a half-inch or less from point to shank from Nov. 1 to Nov. 30 (see pp. 30-31 of the 2025 Michigan Fishing Regulations). Plus, on these same waters, it is unlawful to spear or possess spearing gear from Nov. 1 to Nov. 30 (see pp. 16-17 of the 2025 Michigan Fishing Regulations).
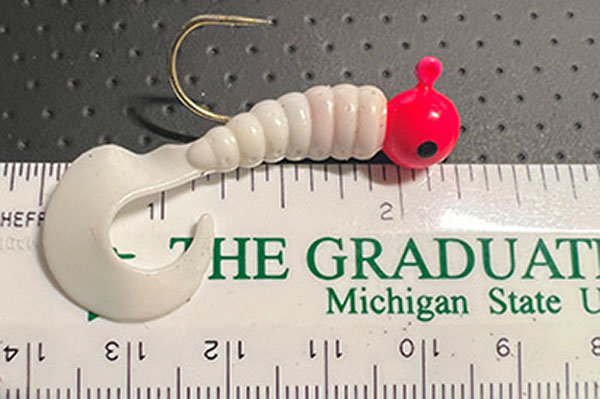
Only single-pointed, unweighted hooks are allowed under these regulations. Single hooks cannot be molded or permanently fixed to a weight or weighted lure. The use of jigs on these waters is prohibited, since they are weighted (metal is molded onto the hook). Lures fished with one single-pointed, unweighted hook would be allowable.
Review the 2025 Michigan Fishing Regulations in the Michigan DNR Hunt Fish app or at Michigan.gov/DNRRegs. To obtain a physical copy of the regulations, reach out to your local DNR Customer Service Center or email MDNR-E-License@Michigan.gov.
Learn more about lake whitefish at Michigan.gov/DNR/Education/Michigan-Species/Fish-Species/Whitefish.
- Details
MDNR Report

When you think of reefs, the Great Lakes don’t immediately come to mind; instead, most people picture the coral reefs associated with tropical waters and colorful fish. But Saginaw Bay once had many rock reefs, created by glacial activity, that provided an important type of habitat for the bay’s aquatic species. Over time, reef habitat was lost, buried by sediment due to logging, manufacturing and agricultural activity in the area. To restore this lost reef habitat, the DNR and many partner organizations worked together on a portfolio of reef habitat projects, including the recently completed Channel Island Reef.
A nearshore reef, Channel Island Reef is constructed in the bay near Channel Island (aka Spoils Island). It is made of natural rock that rises several feet from the bottom but still sits a few feet below the surface of the water. Locally sourced limestone was used, which creates crevices and ledges perfect for spawning fish to deposit eggs into and for young fry (newly hatched fish) to hide from predators. The reef will get lots of wave action, which will keep sediment from building up and wash oxygenated water over fertilized fish eggs, increasing their survival.
“Restoring rocky reefs can help make native fish species – like lake whitefish and walleye – more resilient,” said Jeff Jolley, the DNR’s Southern Lake Huron Fisheries Management Unit manager.
These species use reef habitat for spawning, making it essential for supporting strong fish populations, especially whitefish, which are in decline elsewhere in the Great Lakes.
Jolley said that while walleye are now thriving in the bay, much of the population currently relies on river spawning. That makes it vulnerable—if just one or two river systems experience a disaster, blockage or habitat decline, the effects could ripple across the entire population. By restoring and enhancing diverse spawning habitats, biologists aim to build resiliency into the population.
“It’s similar to diversifying an investment portfolio,” said Jolley. “Spreading the ‘risk’ across multiple spawning areas helps ensure the walleye population remains strong even if one site falters.”
In the coming years, fisheries biologists will study activity at the reef, learning more about how fish use the reef and its beneficial effects on the ecology of Saginaw Bay.
Learn more about the project: Channel Island Reef: Increasing fish spawning habitat and resilience in Saginaw Bay | Michigan Sea Grant.
- Details
MDNR Report

Michigan elk hunters would have longer harvest periods for the 2026-27 hunting cycle under draft proposals by the Michigan Department of Natural Resources.
The proposals would lengthen both elk hunting periods in the northern Lower Peninsula, home to Michigan’s elk herd.
- Hunt Period 1 would run from the second Saturday in September through the second Sunday in October – a 30-day, continuous period. Currently, Hunt Period 1 is broken up into three, four-day hunts stretching across August and September – 12 total hunting days.
- Hunt Period 2 would run from Dec. 1 through Dec. 15 – a 15-day period. Currently, Hunt Period 2 runs from Dec. 13 through Dec. 21 – a nine-day period.
Combined, the two hunting periods would provide 45 total days of harvest time, more than double the current 21 total days of harvest time. The proposals, which do not affect the 2025 elk hunting season, must be approved by the Michigan Natural Resources Commission.
In addition to making Hunt Period 1 longer and continuous, the change would move the period later in the season when the weather is generally colder and better for elk hunting.
“Shifting the period later in the year should give hunters more favorable weather conditions,” said Scott Eggeman, a Gaylord-based field operations manager for the DNR Wildlife Division. “And a monthlong, continuous hunting period would provide hunters with more opportunities, allow flexibility to choose when they want to hunt and help them safety and effectively target an appropriate elk by reducing the pressure on them to make a kill quickly.”
The proposed change to Hunt Period 2 not only lengthens the period but also moves it further away from the Christmas and Hanukkah holidays. Currently, Hunt Period 2 ends Dec. 21; under the proposal, it would end Dec. 15.
In another proposed change, hunters would have 72 hours to register their elk with the DNR. Currently, elk must be registered within 24 hours of harvest.
The draft proposals do not include any recommended changes to Michigan’s elk management unit boundaries or the annual elk drawing.
Feedback on these draft proposals can be emailed to DNR-Elk-Hunt@Michigan.gov by Jan. 23, 2026.
Final proposed elk regulations and elk license quotas for 2026-27 will be presented to the Michigan Natural Resources Commission at its March 2026 meeting. As with all regulations, the final recommendations will be available through a link to the March agenda when it is available on the NRC webpage. Additional input can be provided directly to the NRC at that time.
The final regulations will be adopted at the April 2026 NRC meeting.
- Details
MDNR Report
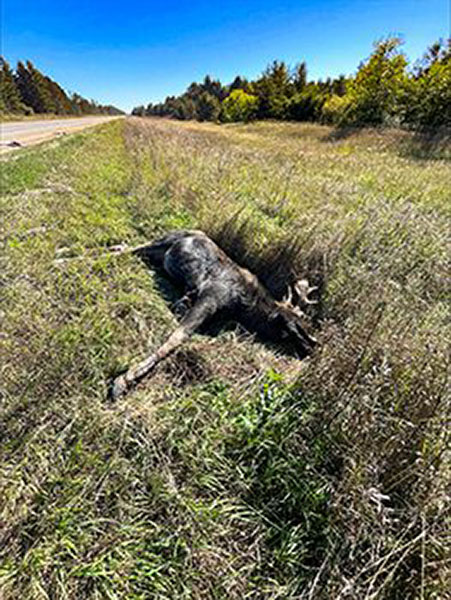

Sixty moose have been killed in vehicle collisions over the past four years in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula, with most of the crashes occurring on stretches of highway in the western U.P.
The fall and summer months, when moose are particularly active, are the most common times for collisions. About a third of all moose deaths from vehicle collisions occur in September and October, according to statistics compiled by the Michigan DNR Wildlife Division and the Michigan Department of Transportation.
On June 17, a female moose raising twin calves was killed by a vehicle at one of the hotspots – U.S. 141 in northern Iron County – likely removing three moose from the population because calves are dependent on their mother.
Over the past decade, the moose population in Michigan’s core range (Baraga, Marquette and Iron counties) has remained between 300 and 500 animals, and DNR wildlife biologists are researching the reasons behind why the population has remained relatively stagnant.
There have been no known human deaths from moose-vehicle collisions, but the potential is always there when a car traveling 55-65 mph or more meets a 1,000-pound animal, said Tyler Petroelje, the DNR’s northern Michigan wildlife research specialist.
“In a sense, Michigan has been very lucky,” Petroelje said. “But at the same time, I think that’s one of those things that is a reality – it could happen at any point.”


